Blockchain Simplified Understanding Digital Ledgers

Decoding Blockchain: Simplified Digital Trust
Introduction: The Buzz Around Blockchain
So, you’ve heard the term “blockchain” thrown around a lot lately. What’s the deal with this technology, and why is everyone talking about it? Let’s break it down in a way that doesn’t require a degree in computer science.
Understanding the Basics: Simplification 101
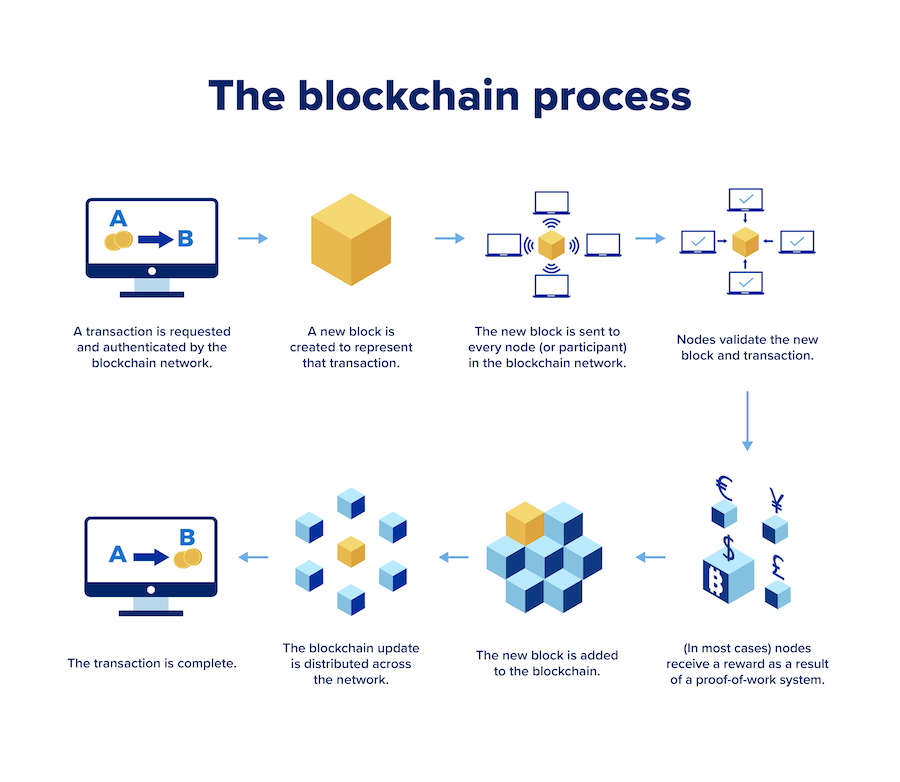
At its core, blockchain is like a super-secure digital ledger. Imagine a record-keeping system that’s not controlled by a single entity but spread across a network of computers. Each record, or “block,” is linked to the one before it, forming an unbreakable chain. This decentralized approach is what makes blockchain unique.
Digital Trust and Security: Blockchain’s Main Gig
Blockchain isn’t just about recording transactions; it’s about building trust in the digital world. The magic happens through a process called cryptography, where complex mathematical algorithms secure each transaction. This makes blockchain not only transparent but also tamper-resistant, adding an extra layer of security to digital interactions.
The Beauty of Decentralization: No Big Brother Here
One of the coolest aspects of blockchain is its decentralization. Traditional systems rely on a central authority—like a bank—to verify and authenticate transactions. With blockchain, that responsibility is distributed across a network of computers, known as nodes. No central authority means more transparency and less dependence on a single entity.
Breaking Down Digital Assets and Smart Contracts
Now, blockchain isn’t just for tracking cryptocurrency transactions. It’s a versatile tool that can represent digital assets and execute smart contracts. Digital assets could be anything from cryptocurrencies to property deeds, all securely recorded on the blockchain. Smart contracts, meanwhile, are self-executing contracts with terms directly coded into the system, automating and enforcing agreements.
The Role of Consensus Mechanisms: Keeping Everyone in Check
For a decentralized system like blockchain to work, everyone needs to be on the same page. That’s where consensus mechanisms come in. These mechanisms ensure that all the nodes on the network agree on the validity of transactions and their order. It’s like a digital vote to maintain the integrity of the system.
Challenges and Solutions: The Realities of Blockchain
Despite its awesomeness, blockchain isn’t without challenges. Scalability, or the ability to handle a growing network, is a concern. Consensus mechanisms, like the energy-intensive Proof of Work, have their downsides. But fear not, because ongoing research and innovation are tackling these challenges head-on.
Real-world Applications: Beyond Cryptocurrency
Blockchain isn’t confined to the realm of cryptocurrencies. Its applications extend across various industries. From supply chain management and healthcare to finance and voting systems, blockchain is transforming how data is stored, accessed, and secured in the real world.
Educating the Masses: Making Blockchain Accessible
To truly embrace the potential of blockchain, education is key. Whether you’re a tech guru or a complete newbie, understanding the basics and staying informed about blockchain developments is crucial. It’s a journey of continuous learning and engagement with the ever-evolving technology.
Embracing the Future: Simplified Blockchain for All
In essence, blockchain is more than just a buzzword; it’s a transformative