Understanding Blockchain A Simple Guide for Beginners
Understanding Blockchain: A Simple Guide for Beginners
So, you’ve heard the buzz about blockchain, and your curiosity is piqued. What is this technology that’s making waves in the digital realm? Let’s break it down in plain and simple terms.
The Basics of Blockchain
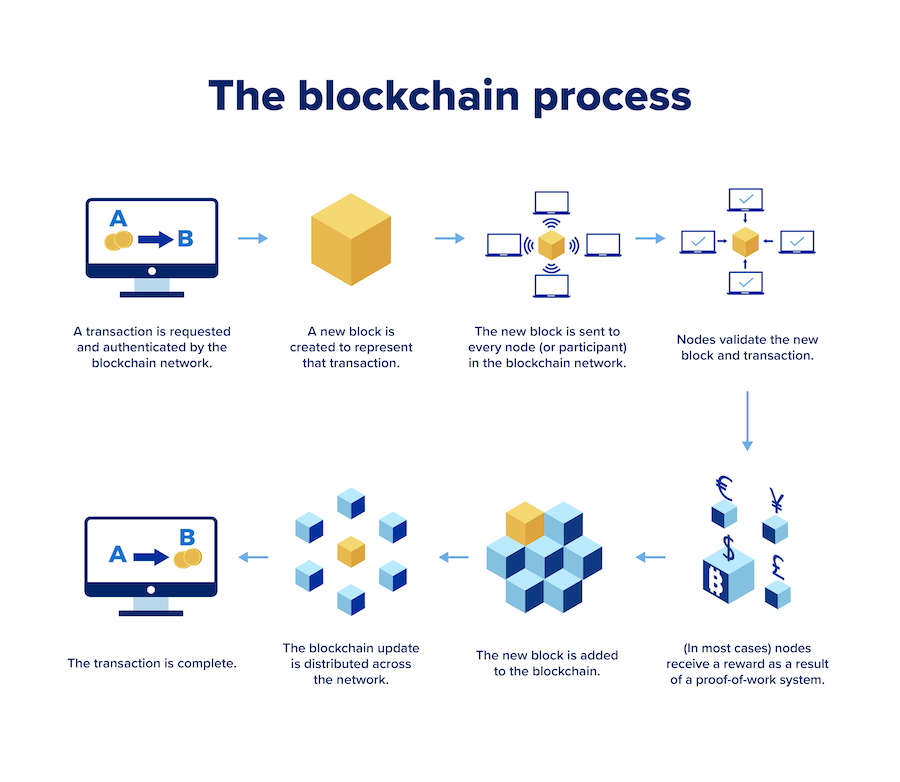
Imagine a digital ledger – a secure, decentralized database shared among a network of computers. This is the essence of blockchain. Each block in this chain contains a list of transactions, and once a block is completed, it’s linked to the previous one, creating a chain of blocks. This chain is maintained across a network of computers, making it resistant to tampering and fraud.
Decoding Digital Ledger Technology
At the core of blockchain is the concept of a digital ledger. Unlike traditional ledgers that are centralized and controlled by a single entity, a blockchain ledger is distributed across a network. This decentralization ensures transparency and removes the need for a central authority, like a bank or government, to oversee transactions.
The Role of Cryptography in Blockchain
Cryptography plays a crucial role in securing the information within each block. Transactions are secured through complex mathematical algorithms, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of the data. This secure layer of cryptography is what makes blockchain an appealing technology for securing digital transactions.
Understanding Decentralization
One of the key features of blockchain is its decentralized nature. Traditional systems rely on a central authority to validate and authenticate transactions. Blockchain, on the other hand, distributes this responsibility across a network of computers, known as nodes. This decentralized approach not only enhances security but also promotes a trustless environment.
Digital Assets and Smart Contracts
Blockchain extends beyond just currency transactions. It enables the creation of digital assets and smart contracts. Digital assets, represented on the blockchain, can include anything from cryptocurrencies to property deeds. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, automating and enforcing the terms without the need for intermediaries.
The Importance of Consensus Mechanisms
For a decentralized system to function effectively, a consensus mechanism is crucial. This mechanism ensures that all nodes on the network agree on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the blockchain. Common consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (used by Bitcoin) and Proof of Stake, each with its own set of advantages and limitations.
Challenges and Scalability
While blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, it’s not without its challenges. Scalability is a notable concern, especially as the network grows. The time and energy required for consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work, can slow down transaction processing. Innovations and ongoing research aim to address these challenges and enhance blockchain’s scalability.
Real-world Applications of Blockchain
Beyond its roots in cryptocurrencies, blockchain is finding applications in various industries. From supply chain management and healthcare to finance and voting systems, the technology is revolutionizing the way data is stored, accessed, and secured. The immutable nature of the blockchain ensures transparency and traceability in these applications.
Educating







