Immutable Ledger Magic Blockchain’s Unchanging Revolution
Decoding the Immutable: Blockchain’s Unalterable Power
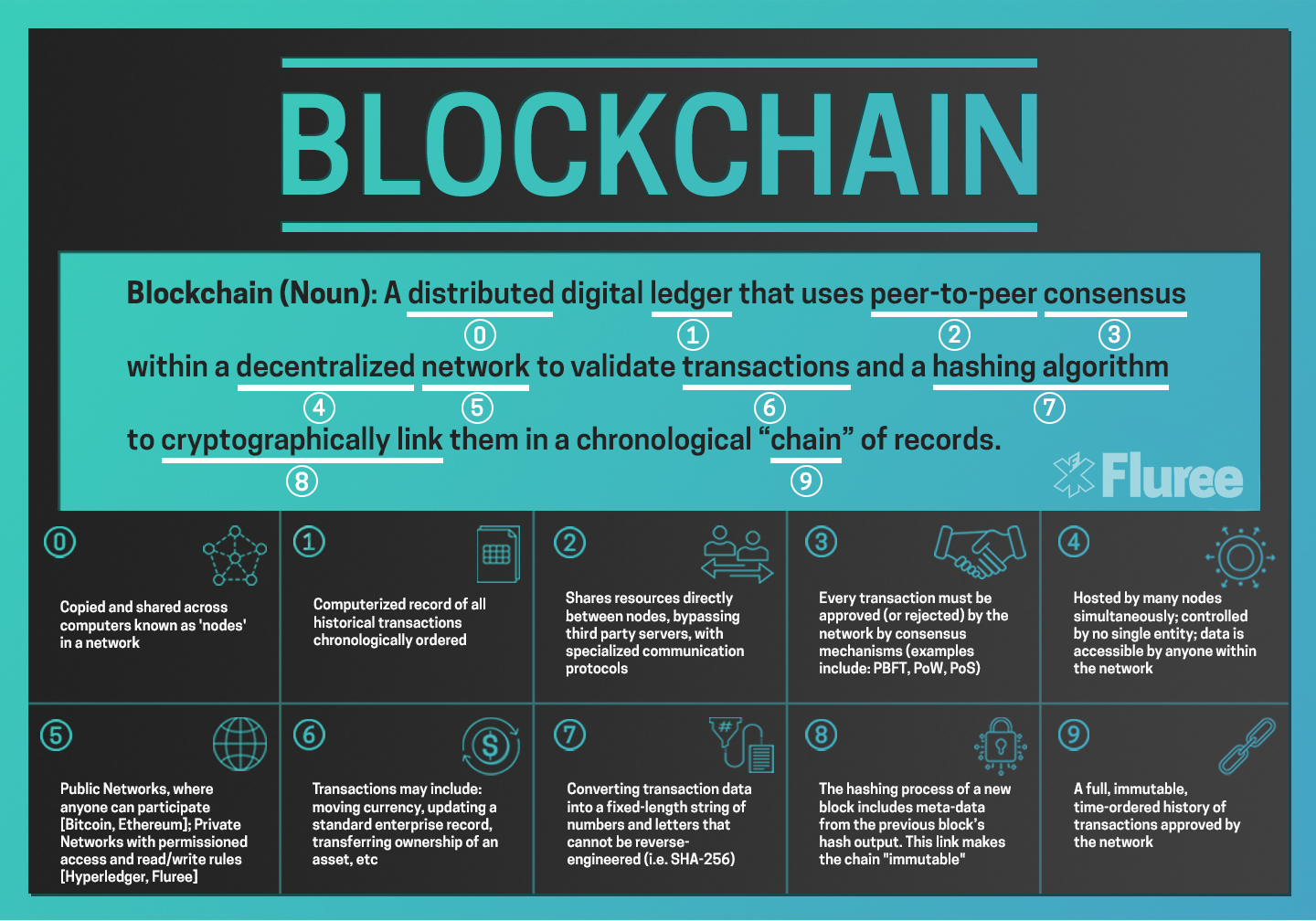
In the dynamic landscape of technology, one term that stands out is “immutable,” and nowhere is this more evident than in the realm of blockchain. This digital marvel brings forth a revolutionary concept – the ability to create an unchanging, tamper-proof ledger that has far-reaching implications across various sectors.
Unveiling Blockchain’s Immutable Charm and Security
At the core of blockchain’s allure is its immutability, a quality that sets it apart from traditional databases. Unlike conventional systems where data can be altered or deleted, blockchain’s architecture ensures that once a block is added to the chain, its contents remain unaltered. This inherent security feature has profound implications for industries requiring transparency and trust.
Immutable Triumph: Blockchain’s Enduring Digital Legacy
Blockchain’s triumph lies in its ability to create an enduring digital legacy. This immutability is particularly crucial in fields like finance and healthcare, where maintaining accurate and unmodifiable records is paramount. The unchangeable nature of blockchain ensures the integrity of transactions and the security of sensitive information, heralding a new era in data management.
The Invincible Blockchain: Embracing the Immutable Era
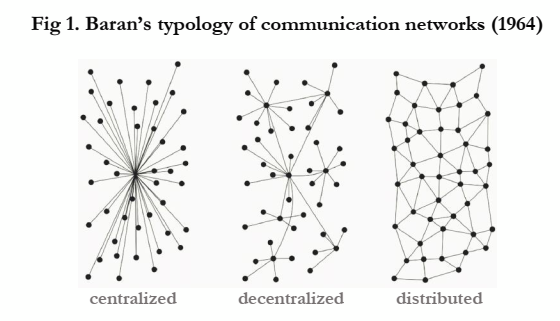
As we embrace the immutable era, blockchain emerges as an invincible force reshaping the digital landscape. The technology’s decentralized and distributed nature, coupled with immutability, ensures that no single entity can control or manipulate the data within the blockchain. This not only enhances security but also fosters a sense of trust among users.
Secure and Immutable: Blockchain’s Unyielding Evolution
Security is the linchpin of blockchain’s unyielding evolution. Its immutability guards against fraud, tampering, and unauthorized access. Whether in financial transactions, supply chain management, or voting systems, the unalterable nature of blockchain provides a secure foundation for processes that demand the highest levels of integrity.
Embracing Immutability: Blockchain’s Unalterable Promise
The promise of immutability in blockchain is not just a technological concept; it represents a shift in how we perceive and interact with digital information. This unalterable promise instills confidence in users, encouraging widespread adoption across industries seeking reliability and permanence in their digital records.
The Permanence of Power: Blockchain’s Immutable Domain
Immutability grants blockchain the permanence of power in the digital domain. It ensures that historical records, once inscribed on the blockchain, are preserved for eternity. This permanence is particularly advantageous in fields such as historical documentation, where the integrity of records is crucial for preserving our collective past.
Blockchain’s Unchanging Symphony: The Immutable Revolution
The immutable revolution orchestrated by blockchain is akin to a symphony, harmonizing the cacophony of data manipulation concerns. It introduces a melody of permanence and security, transforming how businesses and individuals engage with information. In this unchanging symphony, the notes of trust and reliability resonate prominently.
Unaltered Realms: Exploring Blockchain’s Immutable Future
The future of blockchain unfolds in unaltered realms, where the technology’s immutable nature becomes the bedrock of innovation. As industries explore novel use cases, from authenticating digital assets to ensuring the integrity of scientific research, the immutable future promises a paradigm shift in how we handle and safeguard