What to Do Before You Reformat Your Hard Drive
What to Do Before You Reformat Your Hard Drive
 Computers play a very important role in our lives today. Almost everyone is now familiar with computers and there are even some that perceive computers as an indispensable part of their daily routine. However, just like any machine, computers are subject to wear and tear and you may need to reformat your hard drive at some later point in time. Before you reformat, there are several things which you need to know and do first.
Computers play a very important role in our lives today. Almost everyone is now familiar with computers and there are even some that perceive computers as an indispensable part of their daily routine. However, just like any machine, computers are subject to wear and tear and you may need to reformat your hard drive at some later point in time. Before you reformat, there are several things which you need to know and do first.
Reformatting the hard drive is what others call the hard option, and this should only be done as a last resort and not mainly taken out of whim. If you are using Windows XP and having the problems such as frequent “blue screen of death” occurrences, missing DLL errors and constant software crashes even after you have performed steps including virus or spyware scanning, defrag, chkdsk, and all other solutions which are available online or on the manual, then you probably need to reformat the hard disk. In short, when you have done everything other than bathing your PC with soap and water, then it is time to consider a reformat.
Before you take out that Windows XP installation CD out that you bought a couple of years back and start the reformatting process, it is always a good idea to create a backup of the important files on your PC. There are several ways to do this, but the simplest form is just to copy all your important files to a high-capacity flash drive or an external hard disk drive.
If you forgot where you put that driver disk that came along with your computer, you should first check the device drivers on your PC by clicking start, then run, and type in dxdiag. It will show you three most important devices on your PC and these are the display, sound, and network devices. You need to take the information that appears under drivers or the name of the device on a piece of paper and then store it in a safe place.
Once you are done with backing up your files and taking note of the drivers, you can now begin the reformat by putting the Windows CD into the tray and rebooting the computer. If your computer comes with a recovery CD, reformatting and installation of some application software would be much easier. Once done, you will notice a significant boost in the performance of your computer. It will be as if the computer that you had when you first opened the box.…


.jpg) Everything now is run by computers. To be able to run the simple computer we must know at least the basics. Computer literacy is the name of the game. We have to educate ourselves with the basic programs and the simple task of knowing the parts of the computer. A computer instructor will teach us the ABCs of the computer!
Everything now is run by computers. To be able to run the simple computer we must know at least the basics. Computer literacy is the name of the game. We have to educate ourselves with the basic programs and the simple task of knowing the parts of the computer. A computer instructor will teach us the ABCs of the computer! The Information Technology revolution has changed the face of the workplace in the recent past, the present, and, with new technological advances evolving rapidly, for the foreseeable future. This poses the same kind of threat that machinery posed during the industrial revolution, in theory the machines are units of production that far outweigh the capabilities of human beings.
The Information Technology revolution has changed the face of the workplace in the recent past, the present, and, with new technological advances evolving rapidly, for the foreseeable future. This poses the same kind of threat that machinery posed during the industrial revolution, in theory the machines are units of production that far outweigh the capabilities of human beings. Since the 1970s, Moore’s Law has successfully predicted the evolution of computer hardware technology. The law essentially describes the number of transistors that can be placed on an integrated circuit, which is a number that has approximately doubled every two years. Moore’s Law, in a broader sense, has also come to encompass the amazing rate that computer technology has advanced over the last several decades.
Since the 1970s, Moore’s Law has successfully predicted the evolution of computer hardware technology. The law essentially describes the number of transistors that can be placed on an integrated circuit, which is a number that has approximately doubled every two years. Moore’s Law, in a broader sense, has also come to encompass the amazing rate that computer technology has advanced over the last several decades. The last two decades have experienced the electrifying boom in the world of IT with billions of people around the globe relying increasingly on computer technology. Almost all businesses therefore expect at least a little IT or computer support which is great news for anyone who is IT qualified! The more that technology improves and grows, the more jobs in the IT field also arise, hence one of the number 1 reasons why IT courses are being given encouragement and priority in most countries worldwide.
The last two decades have experienced the electrifying boom in the world of IT with billions of people around the globe relying increasingly on computer technology. Almost all businesses therefore expect at least a little IT or computer support which is great news for anyone who is IT qualified! The more that technology improves and grows, the more jobs in the IT field also arise, hence one of the number 1 reasons why IT courses are being given encouragement and priority in most countries worldwide.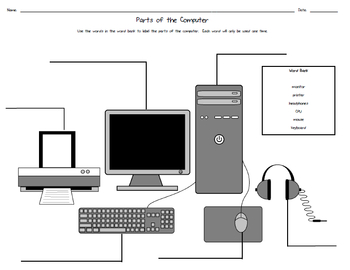 What Is Computer Assisted Surgery?
What Is Computer Assisted Surgery? Staying in touch with all the latest technology news is crucial in the modern society we live in so knowing how you can get the latest stories could prove to be an excellent advantage for anybody. To be able to keep yourself up to date you must come across some reliable technology news sources that can give you timely information. Probably the most well-known news sources for technology news are TV shows, tech magazines and also the world wide web. From each of them it is possible to find out loads of new information and facts, however, many of those sources are much better than others and we’ll explain you why, exactly.
Staying in touch with all the latest technology news is crucial in the modern society we live in so knowing how you can get the latest stories could prove to be an excellent advantage for anybody. To be able to keep yourself up to date you must come across some reliable technology news sources that can give you timely information. Probably the most well-known news sources for technology news are TV shows, tech magazines and also the world wide web. From each of them it is possible to find out loads of new information and facts, however, many of those sources are much better than others and we’ll explain you why, exactly. Today, your business needs are changing fast. You need to move fast to catch up with the latest trends in computer technology. Right use of latest computer technology can be the single largest important factor for your business success.
Today, your business needs are changing fast. You need to move fast to catch up with the latest trends in computer technology. Right use of latest computer technology can be the single largest important factor for your business success. If you’re like many small business owners, you’ve probably wondered about how to accept credit cards from your customers. The problem is that it’s sometimes hard to get a merchant account. They often want a lot of money, and want your credit to be spotless, etc. But, it doesn’t have to be that way.
If you’re like many small business owners, you’ve probably wondered about how to accept credit cards from your customers. The problem is that it’s sometimes hard to get a merchant account. They often want a lot of money, and want your credit to be spotless, etc. But, it doesn’t have to be that way. Computers are used in virtually every business and home across the United States. Business professionals and individuals may know how to use a computer to accomplish all of their needs but many people are lost when it comes to fixing a computer error or creating an information system. This is why online learning in computer technology is beneficial.
Computers are used in virtually every business and home across the United States. Business professionals and individuals may know how to use a computer to accomplish all of their needs but many people are lost when it comes to fixing a computer error or creating an information system. This is why online learning in computer technology is beneficial. IBM (International Business Machines Corporation), also known as ‘Big Blue’, first originated in the late eighteen hundreds far before computers were even being built or used. Now, as the IT consulting and computer technology company it is today, one rarely looks back upon their small beginnings. It has been one hundred years since IBM stepped into the technology world as the company they are today; and even now, they are still wowing their audience of tech gurus with new and improved technology systems every day.
IBM (International Business Machines Corporation), also known as ‘Big Blue’, first originated in the late eighteen hundreds far before computers were even being built or used. Now, as the IT consulting and computer technology company it is today, one rarely looks back upon their small beginnings. It has been one hundred years since IBM stepped into the technology world as the company they are today; and even now, they are still wowing their audience of tech gurus with new and improved technology systems every day. You can gather, organize, and evaluate information pretty conveniently by a RDBMS package that thrives on ease of use and flexibility. The ease of use is one thing which is common to all RDBMS packages today. By organizing your data into relational tables, you make savings on repetitive punching. You also make savings on disk space and labor cost. But more importantly, you now organize your data in a logical compact manner. This reflects logical approach on your part when it comes to making an entry for a transaction as well as locating and retrieving information. Good analysis of data can provide you information on valuable hidden trends: You can accordingly tune yourself to grow your future business.
You can gather, organize, and evaluate information pretty conveniently by a RDBMS package that thrives on ease of use and flexibility. The ease of use is one thing which is common to all RDBMS packages today. By organizing your data into relational tables, you make savings on repetitive punching. You also make savings on disk space and labor cost. But more importantly, you now organize your data in a logical compact manner. This reflects logical approach on your part when it comes to making an entry for a transaction as well as locating and retrieving information. Good analysis of data can provide you information on valuable hidden trends: You can accordingly tune yourself to grow your future business. Most people want flexibility when working with a computer or laptop. This is a very possible, thanks to the progress of computer technology. Many hardware and software applications continue emerging to make user experience more fulfilling. For instance, an usb port replicator is a small hardware gadget that many people long for. It actually works best for people who prefer using both desktop computers and laptops.
Most people want flexibility when working with a computer or laptop. This is a very possible, thanks to the progress of computer technology. Many hardware and software applications continue emerging to make user experience more fulfilling. For instance, an usb port replicator is a small hardware gadget that many people long for. It actually works best for people who prefer using both desktop computers and laptops. If you haven’t familiarized yourself with remote desktop control software, then now is the time to do just that. With a few quick and simple relations, you can make your work life much easier, and make some of your personal things that you do with your computer that much more efficient and practical.
If you haven’t familiarized yourself with remote desktop control software, then now is the time to do just that. With a few quick and simple relations, you can make your work life much easier, and make some of your personal things that you do with your computer that much more efficient and practical. Just like any other machine, computers are prone to breaking down at any time. This can cause inconvenience to one especially if they had important data or information stored in it. Therefore there is need for this to be prevented at any cost. One way of doing this is by the use of computer preventive maintenance software and utilities.
Just like any other machine, computers are prone to breaking down at any time. This can cause inconvenience to one especially if they had important data or information stored in it. Therefore there is need for this to be prevented at any cost. One way of doing this is by the use of computer preventive maintenance software and utilities. As a child, John Halamka was passionate about science and electronics. In 4th grade, he presented a home-built Van de Graff generator at his school science fair and took home first place honors. Fast forward 30 some years, and Halamka, now Dr. Halamka is the chief information officer at Harvard medicine school. Dr. Halamka is not only the acting CIO, but is also a practicing emergency-ward physician and electronic health records advisor for the Obama administration.
As a child, John Halamka was passionate about science and electronics. In 4th grade, he presented a home-built Van de Graff generator at his school science fair and took home first place honors. Fast forward 30 some years, and Halamka, now Dr. Halamka is the chief information officer at Harvard medicine school. Dr. Halamka is not only the acting CIO, but is also a practicing emergency-ward physician and electronic health records advisor for the Obama administration. Computers and Older Users
Computers and Older Users
 Soon schools and colleges will start back after long holidays, back to study, revision and cramming. What if I could give you information on how to make studying and more importantly revising for exams easier, quicker and fun? I am not saying that studying will become a breeze but that revision of notes and cramming will flow better and simpler. This is what I would have loved to have known about in university, as I found revising my cramped notes and illegible handwriting very difficult.
Soon schools and colleges will start back after long holidays, back to study, revision and cramming. What if I could give you information on how to make studying and more importantly revising for exams easier, quicker and fun? I am not saying that studying will become a breeze but that revision of notes and cramming will flow better and simpler. This is what I would have loved to have known about in university, as I found revising my cramped notes and illegible handwriting very difficult. Unemployment is leaving a very negative impact on the economies of different nations. While developing countries continue its struggle to create more jobs, developed nations are finding it difficult to offer jobs. Therefore there is a lot of gap between developing nations and developed nations and this bridge of gap must be reconnected in order to ensure that jobs are everywhere and people find it quite convenient to find jobs.
Unemployment is leaving a very negative impact on the economies of different nations. While developing countries continue its struggle to create more jobs, developed nations are finding it difficult to offer jobs. Therefore there is a lot of gap between developing nations and developed nations and this bridge of gap must be reconnected in order to ensure that jobs are everywhere and people find it quite convenient to find jobs. Remember those days when we used to walk in to the banks and get our pass books filled manually or the supermarkets, where we used to get hand written bills and the counter staff would sit with the help of a calculator and total up the bill.
Remember those days when we used to walk in to the banks and get our pass books filled manually or the supermarkets, where we used to get hand written bills and the counter staff would sit with the help of a calculator and total up the bill. How did the computer games become so popular among the teens?
How did the computer games become so popular among the teens? Your computer forum updates you with all the new computer products and services that are in the offerings for your better use of resources. You get technical support for installing, upgrading computer peripherals and accessories like computer printer, Wi-Fi, digital camera, etc.
Your computer forum updates you with all the new computer products and services that are in the offerings for your better use of resources. You get technical support for installing, upgrading computer peripherals and accessories like computer printer, Wi-Fi, digital camera, etc. Today, tech savvy new age learners visit tech support forum frequently and keep on weighing newer options. They know that to gather any new significant breakthrough in big lead they have to constantly be on search. A good tech support forum helps them in their search. You too can opt for this cheap free online source available to you 24×7 that will help you in coming through a set of important ideas put together in one piece. This also brings what many good tech help learners see as clarity on understanding in providing them better precision on tech support needs of the day.
Today, tech savvy new age learners visit tech support forum frequently and keep on weighing newer options. They know that to gather any new significant breakthrough in big lead they have to constantly be on search. A good tech support forum helps them in their search. You too can opt for this cheap free online source available to you 24×7 that will help you in coming through a set of important ideas put together in one piece. This also brings what many good tech help learners see as clarity on understanding in providing them better precision on tech support needs of the day. Organizations of higher learning are still not in agreement of what is meant by many technical levels, such as application technological innovation and PC technological innovation. These areas, along with it, computer, and PC technological innovation technological innovation, are simply too new. Therefore, what one school or employer thinks as a requirement PC technological innovation may be viewed by another as application technological innovation? In the start, computer systems were hard-wired to perform a certain function. The individual did little more than impact a button. Allowing greater individual management led to the progression of coding dialects and compilers to change “normal” terminology into PC terminology. On-line began to come into its own with the progression of the laptop or PC. Simple dialects such as BASIC gave more management to the average individual. This laid the fundamentals for the application professional, who not only understands the program but the physical abilities of the hardware. One method of analyzing the variations between application technological innovation and PC technological innovation is to consider how most models were managed by the first PCs.
Organizations of higher learning are still not in agreement of what is meant by many technical levels, such as application technological innovation and PC technological innovation. These areas, along with it, computer, and PC technological innovation technological innovation, are simply too new. Therefore, what one school or employer thinks as a requirement PC technological innovation may be viewed by another as application technological innovation? In the start, computer systems were hard-wired to perform a certain function. The individual did little more than impact a button. Allowing greater individual management led to the progression of coding dialects and compilers to change “normal” terminology into PC terminology. On-line began to come into its own with the progression of the laptop or PC. Simple dialects such as BASIC gave more management to the average individual. This laid the fundamentals for the application professional, who not only understands the program but the physical abilities of the hardware. One method of analyzing the variations between application technological innovation and PC technological innovation is to consider how most models were managed by the first PCs. Has your PS3 refused to come on? Do you think your PS3 has developed the dreaded yellow light of death? Would you like some help on how to fix yellow light of death right now? We all hate it when we invite our friends home or just want to have a little fun playing our favourite games and the PS3 gets whacked. It’s an annoying feeling that sometimes makes you feel like throwing it out the window. But, you don’t have to do that; you can learn how to fix the yellow light of death and repair the console pretty quickly. To do this, here are a few tips
Has your PS3 refused to come on? Do you think your PS3 has developed the dreaded yellow light of death? Would you like some help on how to fix yellow light of death right now? We all hate it when we invite our friends home or just want to have a little fun playing our favourite games and the PS3 gets whacked. It’s an annoying feeling that sometimes makes you feel like throwing it out the window. But, you don’t have to do that; you can learn how to fix the yellow light of death and repair the console pretty quickly. To do this, here are a few tips Today computer is something by which we cannot do with. You use computer for a host of your offline as well as online interactive activities.
Today computer is something by which we cannot do with. You use computer for a host of your offline as well as online interactive activities.




